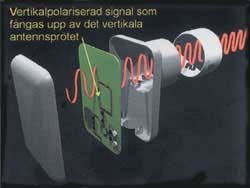
The satellites broadcast with polarized radio waves and many of them with so-called linear polarization. This means that the
electric respective the magnetic wave movement happens in a certain plane.
The satellites broadcast with polarized radio waves and many of them with so-called linear polarization. This means that the
electric respective the magnetic wave movement happens in a certain plane.A signal that is horizontally polarized is entirely isolated from a signal that is vertically polarized, even if the signals lie within the same frequency range. This is very good, because in this way we can use the frequency spectrum two times and thereby its possible to broadcast the twice amount of information. But this also means that the antennas that are used in order to capture the signal must be absolutely correct orientated in ratio to the incoming signals polarized directions. Otherwise will the horizontal- and vertical polarized signals will mix with each other.
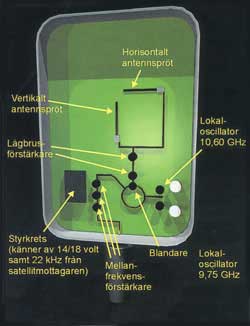
In order to illustrate this we shall look a little closer on how a LNB works. LNBn is a small unit, which the
distinctive part is the feedhorn that is a circular tapered pipe. The broad part of the tapered is covered
with a window, Each of the switch diodes can either be under current, then they let the signal through, or other wise they blocks the signal. In this way we can control which of the both the Arial rods that shall be used.
The two a low noise transistor are the most important component in entire LNBn. It's the development of the low noisiness in these
transistors that have made it possible to have small and practical satellite dishes. There are also two local oscillator that can be connected in and out if needed. Finally there is also a so called middle frequency amplifier, that reinforces the mixed signal additional 1000 times, within frequency spectrum 950-2150 MHz, Then the signal will be sent further to satellite receiver.
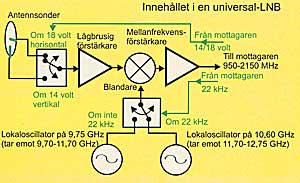
In order to get a good result with your satellite dish installation is it very important that the LNBn is Here below can you see schematic for a universal LNB.
|
 which most often is made of a plastic material, which drops through the microwave signal. The signal is
lead by the feed horn into the actual circuit card, in which two small Arial rods are etched. Arial rods of this the
type is a quartz wavelength. Because the transmission frequency from the satellites usually lie round 12 GHz (12000 MHz), means
this a wavelength of approx 2,5 centimetre. There for the small Arial rods become approx 6 mm long. They are linked to switch
diodes with help of a low noise amplifier, that amplifies the signal approx 100 times.
which most often is made of a plastic material, which drops through the microwave signal. The signal is
lead by the feed horn into the actual circuit card, in which two small Arial rods are etched. Arial rods of this the
type is a quartz wavelength. Because the transmission frequency from the satellites usually lie round 12 GHz (12000 MHz), means
this a wavelength of approx 2,5 centimetre. There for the small Arial rods become approx 6 mm long. They are linked to switch
diodes with help of a low noise amplifier, that amplifies the signal approx 100 times. After low noise amplifier there is a mixer, there the incoming signal are mixed with either frequency 9,75 GHz or 10,60 GHz,
depending on in which part of the frequency spectrum (10,70-12,75 GHz) that the signal lies, which you want to receive.
After low noise amplifier there is a mixer, there the incoming signal are mixed with either frequency 9,75 GHz or 10,60 GHz,
depending on in which part of the frequency spectrum (10,70-12,75 GHz) that the signal lies, which you want to receive.